First Aid
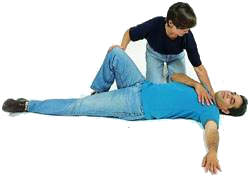
The recovery position
The following is a guide to placing an adult or child (above the age of 1 year) in the recovery position.
If casualty has head or neck injuries:
- Ensure head and neck are supported at all times.
- Do not allow rotation between head and spine.
- Do not tilt head back if neck injury suspected.
Step 1 - Position the casualty's legs
- Kneel beside the casualty.
- Straighten the casualty's limbs.
- Lift the nearer leg at the knee so that it is bent.
Step 2 - Position the casualty's arms
- Place the casualty's nearer arm across their chest.
- Place the other arm at right angles to their body.
Step 3 - Roll the casualty into position
- Roll the casualty away from you onto their side.
- Keep their leg at a right angle with the knee touching the ground to prevent the casualty rolling onto their face.
- For a child, extend both their arms perpendicular to their body.
Step 4 - Steady the casualty
- Make any adjustments necessary to ensure the casualty does not roll.
Step 5 - Ensure the airway is open
Fainting
A faint is a brief loss of consciousness of no more than momentary duration caused by a temporary reduction in the flow of blood to the brain. Recovery is usually rapid and complete.
It may be a nervous reaction to pain or fright; or the result of an emotional upset, exhaustion or lack of food. It is, however, more common after long periods of physical inactivity, especially in warm atmospheres, where lack of muscular activity causes a large volume of blood to collect in the lower part of the body and legs. This reduces the amount of blood available to the circulation, e.g. as in a soldier standing on parade.
Symptoms & Signs
- Pulse will be slow at first (this is an important clue) and weak.
- Casualty may be very pale.
Aim
Position the casualty so that gravity helps increase the flow of blood to the brain.
Prevention
If the casualty is on parade or standing in a crowd, advise him or her to flex the leg muscles and toes to aid circulation.
If the casualty feels unsteady, sit them down and help them to lean forward with their head between their knees and advise them to take deep breaths.
Treatment
- When a casualty faints, lay them down with their legs raised and maintain an open airway.
- Loosen any tight clothing at their neck, chest and waist to assist circulation and breathing.
- Make sure that the casualty has plenty of fresh air; place them in a current of fresh air and fan air onto their face. If necessary, place them in the shade.
- Reassure them whilst they are regaining consciousness; gradually raise them to a sitting position.
- Check for and treat any injury that they may have sustained on falling.
- Check breathing rate, pulse and level of responsiveness until fully recovered.
Burns and Scalds
Burns and scalds must be cooled as soon as possible in order to prevent further damage to underlying tissues and to alleviate pain, swelling and the possibility of shock. The most effective method of cooling is to flood the area gently with cold water.
Any clothing which has been soaked in boiling fluid should be removed as soon as it begins to cool. Cooled, dry, burnt clothing should not be removed because doing so may introduce an infection.
Very small burns or scalds can generally be treated on site. However, if you are in any doubt about the severity of the injury, or if the casualty is an infant ot a sick or elderly person, always seek medical advice.
Friction burns should be treated as minor burns unless the skin is broken, in which case they should be treated the same as minor external bleeding.
Symptoms & Signs
- Severe pain in and around the injured area.
- Redness and possible swelling of the area and sometimes peeling of the skin and blisters, which may be broken.
- In deeper burns the skin may appear grey, pale or waxy, or may be charred. There may be areas of numbness.
- Symptoms and signs of shock which may be delayed. The degree of shock will relate to the extent of the injury.
Aim
Reduce the effect of the heat, prevent infection, relieve pain and minimise shock. Arrange urgent removal to hospital if the burns are severe or extensive.
Treatment - minor burns and scalds
- Reassure the casualty. Place the injured part under slowly running cold water or immerse it in cold water at least 10 minutes - longer if pain persists because the heat may not have been sufficiently withdrawn from the burnt area causing the tissues to continue to "cook".
- Gently remove any rings, watches, belts, shoes or other constricting clothing from the injured area before it starts to swell.
- Dress the area with clean, preferably sterile, non-fluffy material.
DO NOT break blisters, remove any loose skin or otherwise interfere with the injured area.
DO NOT apply lotions, ointments or fat to the injury.
DO NOT use adhesive dressings.
- If in doubt about the severity of the injury, seek medical aid.
Treatment - severe burns and scalds
- Lay the casualty down. Protect the burnt area from contact with the ground, if possible. If the burnt area is still hot, carefully pour jugs of cold water or suitable cold liquid over the burnt area and continue until the pain has stopped.
- Gently remove any rings, watches, belts or constricting clothing from the injured area before it starts to swell.
- Carefully remove any clothing soaked in boiling fluid after it has begun to cool.
DO NOT remove anything this is sticking to a burn.
- Cover the injured area with a sterile dressing or similar non-fluffy material. A clean, preferably new plastic bag may be used for an injured hand or foot, Secure with a bandage.
- For facial burns indoors, cool with water until pain is relieved. No cover is usually required. Alternatively, make a mask from a clean, dry, preferably sterile piece of material with holes for the nose, mouth and eyes.
- Immobilise a badly burned limb.
- If the casualty has become unconscious, open their airway and check breathing. Complete the ABC of breathing and place them in the recovery position.
- Arrange urgent removal to hospital, maintaining the treatment position. Transport as a stretcher case if necessary.
Epilepsy
This is a condition which results from a tendency towards brief disruptions in the normal electrical activity of the brain. Epileptic fits may vary from momentary inattention without loss of consciousness (minor epilepsy) to muscular spasm and convulsions (major epilepsy).
Minor Epilepsy
Symptoms & Signs
- Casualty may appear to be in a daydream and be staring ahead blankly.
- Casualty might start behaving strangely; these "automatisms" include chewing or smacking lips, saying odd things or fiddling with clothing.
- Casualty may have lost memory.
Aim
Protect the casualty while consciousness is impaired.
Treatment
- Protect the casualty from any dangers such as busy roads. Keep other people away from them. Talk to them quietly.
- Stay with them until you are certain that they have recovered and can get home.
NOTE: It is not unusual for a major fit to follow a minor one.
- Advise the casualty to see a doctor.
Major Epilepsy
Symptoms & Signs
- Casualty suddenly loses consciousness and falls to the ground, sometimes letting out a strange cry.
- The casualty becomes rigid for a few seconds and breathing may cease. Mouth and lips turn blue (cyanosis) and there will be congestion about the face and neck.
- The muscles then relax and begin convulsive or jerkin movements. These convulsions may be quite vigorous.
- During this stage the breathing may be difficult or noisy through the clenched jaw; froth may appear around the mouth - it may be bloodstained if lips or tongue have been bitten; and there may be loss of control of the bladder and occasionally the bowel.
- Finally, the muscles will relax although the casualty will remain unconscious for a few minutes more.
- After the fit is over, usually no more than five minutes later, breathing will return to normal and the casualty will regain consciousness but may be dazed and confused and act strangely. This can last from several minutes to an hour and the person may want to rest quietly.
Aim
Protect the casualty from injury during the fit and provide care once they have regained consciousness.
Treatment
- If the casualty is falling, try to support them or ease their fall and lay them down gently, in a safe place if possible.
- Clear a space around the casualty and, unless you want someone to help, ask all bystanders to leave. If possible, carefully loosen clothing around the neck and place something soft under their head.
DO NOT move or lift the casualty unless in danger.
DO NOT forcibly restrain them.
DO NOT put anything in their mouth or try to open it.
DO NOT try to wake the casualty.
- When the convulsions cease, place the casualty in the recovery position to aid their breathing.
- When the attack is over stay with the casualty until you are certain recovery is complete.
DO NOT give the casualty anything to drink until you are sure of full alertness.
- Even if they make a full, quick recovery, advise them to inform their doctor about the latest attack.
DO NOT send for an ambulance unless the casualty has been injured during the fit or takes longer than 15 minutes to regain consciousness. If they have an epilepsy card, it may tell you how long they normally take to wake up.
Bleeding
Minor Bleeding
Symptoms & Signs
- Pain at the site of the wound.
- Steady trickle of mixed blood.
Aim
Control bleeding and minimising infection.
Treatment
- If possible wash your hands before dealing with the wound. Then, if the wound is dirty, lightly rinse it with running water, if available, until it is clean.
- Temporarily protect the wound with a sterile swab. Carefully clean the surrounding skin with the water and soap if available. Gently wipe away from the wound using each swab once only and taking care not to wipe off any blood clots. Dab gently to dry.
- If bleeding persists, apply direct pressure.
- Cover a small wound with an appropriate dressing.
- Raise and support the injured part.
- If in any doubt about the injury, seek medical aid.
Major Bleeding
Symptoms & Signs
- Evidence of major external blood loss.
- Symptoms and signs of shock.
- Casualty feels faint and giddy.
- Face and lips become pale.
- Skin feels cold and clammy.
- Pulse becomes faster but weaker.
- Casualty may become restless and talkative.
- Casualty may complain of thirst.
- Breathing may become shallower.
- Vision may be blurred.
- Possible unconsciousness.
Aim
Control bleeding and minimise the risk of infection. Arrange urgent removal to hospital.
Treatment
- Expose the wound and look for foreign bodies. Apply direct pressure to control bleeding by pressing with your fingers or palm of your hand over a clean dressing. If no dressing is available, use your bare hands. Alternatively, ask the casualty to use their hand. If the wound is gaping, squeezing the edges together may be more effective.
- Raise and support the part if the wound is on a limb.
- Place a sterile or clean dressing and padding over the wound, making sure that it extends well beyond the edges of the wound. Press down firmly and secure with a bandage. Tie bandage firmly enough to control bleeding but not so tight as to cut of circulation. Immobilise the injured part.
- If bleeding continues, do not remove dressing, but apply further dressing or pads on top of the original ones and bandage firmly.
If the injury is on a limb and direct pressure and elevation is ineffective, apply direct pressure to the main artery which supplies the limb.
DO NOT apply indirect pressure for any longer than 10 minutes, nor apply a tourniquet.
- Arrange urgent removal to hospital.
Hysteria
This is usually caused by an over-reaction to an emotional upset or nervous stress and is likely to be heightened by the presence of any onlookers.
Symptoms & Signs
- Temporary loss of behavioural control with dramatic shouting, screaming, crying and/or wild beating of limbs. Casualty may be rolling around on the ground and/or tearing at hair and clothes.
- Hysterical over-breathing (hyper-ventilation) may follow.
- Casualty may be unwilling to move or be making strange movements.
Aim
Isolate the casualty from any onlookers and gently but firmly help him or her to calm down enough to regain control.
Treatment
- Reassure the casualty, refrain from showing him or her any sympathy and gently but firmly escort to a quiet place.
DO NOT physically restrain or slap the casualty; this may make him or her behave more violently.
- Stay with the casualty and keep under observation until fully recovered.
- Advise the casualty to see a doctor.
Heart Attack
This covers coronary thrombosis, coronary obstruction, myocardial infarction and other forms of heart disease.
Symptoms & Signs
- Sudden crushing, vice-like pain in the centre of the chest (sometimes described as severe indigestion) which may spread to the arms, throat, jaw, abdomen or back, and does not subside with rest.
- Sudden dizziness or giddiness causing the casualty to sit down or lean against a wall.
- Skin may be ashen; lips and extremities may become blue (cyanosis).
- Profuse sweating may develop.
- Breathlessness can occur.
- Fast pulse, which becomes weaker and may become irregular.
- Unconsciousness may develop.
- Breathing and heartbeat may stop.
Aim
Minimise the work of the heart and obtain medical aid. Arrange urgent removal to hospital.
Treatment
- If the casualty is conscious, gently support and place them in a half-sitting position with their head and shoulders supported and knees bent.
DO NOT let them move unnecessarily as this will put extra strain on the heart.
- Loosen any constricting clothing around their neck, chest and waist.
- Check breathing rate, pulse and level of responsiveness at 10 minute intervals.
- If they become unconscious, open their airway and check breathing. Complete the ABC of resuscitation if required and place them in the recovery position.
- Arrange urgent removal to hospital. Transport as a stretcher case, maintaining the treatment position.
Cardiac arrest
This is a very serious condition in which the heart suddenly stops beating altogether. It can be the result of an extensive coronary obstruction.
Symptoms & Signs
- Casualty will become unconscious.
- Breathing will be absent.
- Skin will be ashen.
- No pulse will be felt after two inflations of artificial ventilation.
Aim
Begin resuscitation without delay. Arrange urgent removal to hospital making it clear that a heart attack is suspected.
Treatment
- Begin resuscitation immediately.
- Remove to hospital urgently. If necessary, continue resuscitation on the way.
Diabetic Coma
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) may occur when a diabetic has taken too much insulin, missed a meal or exercised such that the concentration of sugar in the blood is diminished. If prolonged or very low, this will result in loss of consciousness and possibly death of the casualty.
Symptoms & Signs
- A diabetic may feel faint, dizzy and light-headed and may be aware that their blood sugar level is low.
- Casualty may be confused and disorientated and may appear to be drunk and possibly agressive.
- Skin becomes pale, with profuse sweating.
- Pulse becomes rapid.
- Breathing becomes shallow and breath will be odourless.
- Limbs may begin to tremble.
- Casualty's level of responsiveness. may deteriorate rapidly.
Aim
Restore the sugar/insulin balance as soon as possible. If the casualty is unconscious, arrange urgent removal to hospital.
Treatment
- If the casualty is conscious and capable of swallowing, immediately give sugar lumps, a sugary drink, chocolate or other sweet food in order to raise the level of sugar in the blood. If the condition improves within a few minutes, give more sweetened food or drink. Instruct the casualty to seek medical advice.
- If the casualty is unconscious, carry out the general treatment for the unconscious casualty. Seek medical aid and arrange urgent removal to hospital.
Nose Bleed
Symptoms & Signs
- Moderate flow of blood from the nose.
- If skull fracture is present, there may be a mixture of blood and clear, watery cerebro-spinal fluid.
Aim
Safeguard the breathing by preventing inhalation of blood, and control bleeding.
Treatment
- Sit the casualty down with their head well forward and loosen any tight clothing around their neck.
- Advise them to breathe through their mouth and to pinch the soft part of the nose.
- Forbid speach, swallowing, coughing, spitting or sniffing. Allow them to dribble and mop it up.
- Release the pressure after 10 minutes. If the bleeding has not stopped, continue treatment for further periods of 10 minutes as necessary.
DO NOT let the casualty raise their head
- While the head is still forward, if possible, get the casualty to gently clean around the nose and mouth using a swab or clean dressing soaked in luke-warm water. Do not plug the nose.
- When the l=bleeding stops, tell the casualty to avoid exertion and not to blow their nose for at least for hours so as not to disturb the clot.
- If after 30 minutes the bleeding persists or recurs, seek medical aid.
Insect Sting
Some people have an allergic reaction to insect sting poison. Multiple stings can therefore have a dangerous cumulative effect.
Symptoms & Signs
- Unexpected sharp pain; an insect may still be present.
- There will be swelling around the affected area with a central reddened puncture point.
- Possibility of shock depending on the degree of reaction.
Aim
Remove sting if present and attempt to reduce swelling and relieve pain. If the sting is inside the mouth, arrange urgent removal to hospital.
Treatment
- If the sting has been left embedded in the skin, hold the tweezers as near to the skin as possible, grasp the sting and remove it.
DO NOT squeeze the poison sac because this will force the remaining poison into the skin
- To relieve pain and swelling, apply a cold compress, surgical spirit or a solution of bicarbonate of soda. For jellyfish stings, smooth calamine lotion into the affected area.
- If pain and swelling persist or increase over the next day or so, advise the casualty to seek medical advice.
- For stings in the mouth, give the casualty ice to suck or rinse their mouth with cold water or a solution of water and bicarbonate of soda. If breathing becomes difficult, place them in the recovery position. Arrange removal to hospital.
Hyperventilation
Symptoms & Signs
- Short, rapid breathing, as if the casualty has been running for a while.
Aim
Calm the casualty so that they can regain control of their breathing and rebalance the level of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
Treatment
- Avoid becoming caught up in the panic (remain calm )
- Make direct eye contact, and speak clearly and slowly.
- Identify yourself if you're not known to the person.
- Give short clear instructions.
- Make calming gestures.
- Allow the casualty some space ( don't crowd them in )
- Minimise embarrassment and avoid an audience.
- Get them to sit down, if they aren't already.
- Sit with them at eye level
- Encourage them to breathe normally. ( talk them through the breathing cycle )
- - Inhale, take in long slow deep breath. ( breathe with them )
- - Hold breath for +1 seconds.
- - Exhale slowly, ( pucker your lips like you're going to kiss )
- - Tell them to relax in a clam voice, just before they reach the end of exhalation.
- Start a new breathing cycle while telling them how well they are doing.
- Continue encouraging them to breathe normally.
Migraine
These severe and sometimes incapacitating headaches can occur for no apparent reasonand cannot normally be traced to any particular disorder. However, they may follow lack of food, noise, heat, travelling or emotional disturbances.
Symptoms & Signs
- Casualty may experience "flickering" vision - this can precede the headache.
- Casualty will be feeling nauseated and may already be vomitting.
- Intense throbbing headache which may only affect one side of the head.
- Casualty cannot tolerate light or noise.
- Casualty may look very pale.
Treatment
- Place a cold compress or covered hot-water bottle on the casualty's forehead, whichever is preferred.
- Advise the casualty to take one or two of their own pain-killing tablets if available.
- If practical, advise the casualty to lie down in a darkened room.
- If the headache persists, or if it is accompanied by a feeling of nausea, vomitting, fever, stiff neck, disturbed vision, obvious head injury, confusion or gradual loss of consciousness, seek medical aid.
Dizziness
Symptoms & Signs
- Casualty is unable to walk straight or stand upright.
- Casualty feels light-headed or experiences a spinning sensation.
- Casualty may experience tinitus or hearing impairment.
Aim
Dizziness is often a symptom for many afflictions or injuries and the casualty to be referred for medical advice as appropriate.
Treatment
- If the symptoms are not temporary, the balance system (i.e. the inner ear) may have been affected. Advise the casualty to seek medical aid or, if they are unable to, arrange for removal to hospital.
- For temporary dizziness, refer to treatment of fainting.